What is Civic Learning?
Civic learning is a process through which young people develop the knowledge, skills, and commitments to interact effectively with fellow community members to address shared problems. It includes preparation for both civic engagement (or practices seeking to promote the public good through non-governmental organizations and informal community work) and political engagement (or activities aiming to influence state action through formal avenues such as voting, lobbying, or petitioning).1 There are many practices that directly improve the quality and effectiveness of civic learning in schools,2 including civic action projects; digital literacy education and engagement; classroom instruction in government, history, law and democracy; discussion of current events; service-learning; extra-curricular or co-curricular activities; student voice in school governance; and simulations of democratic processes.
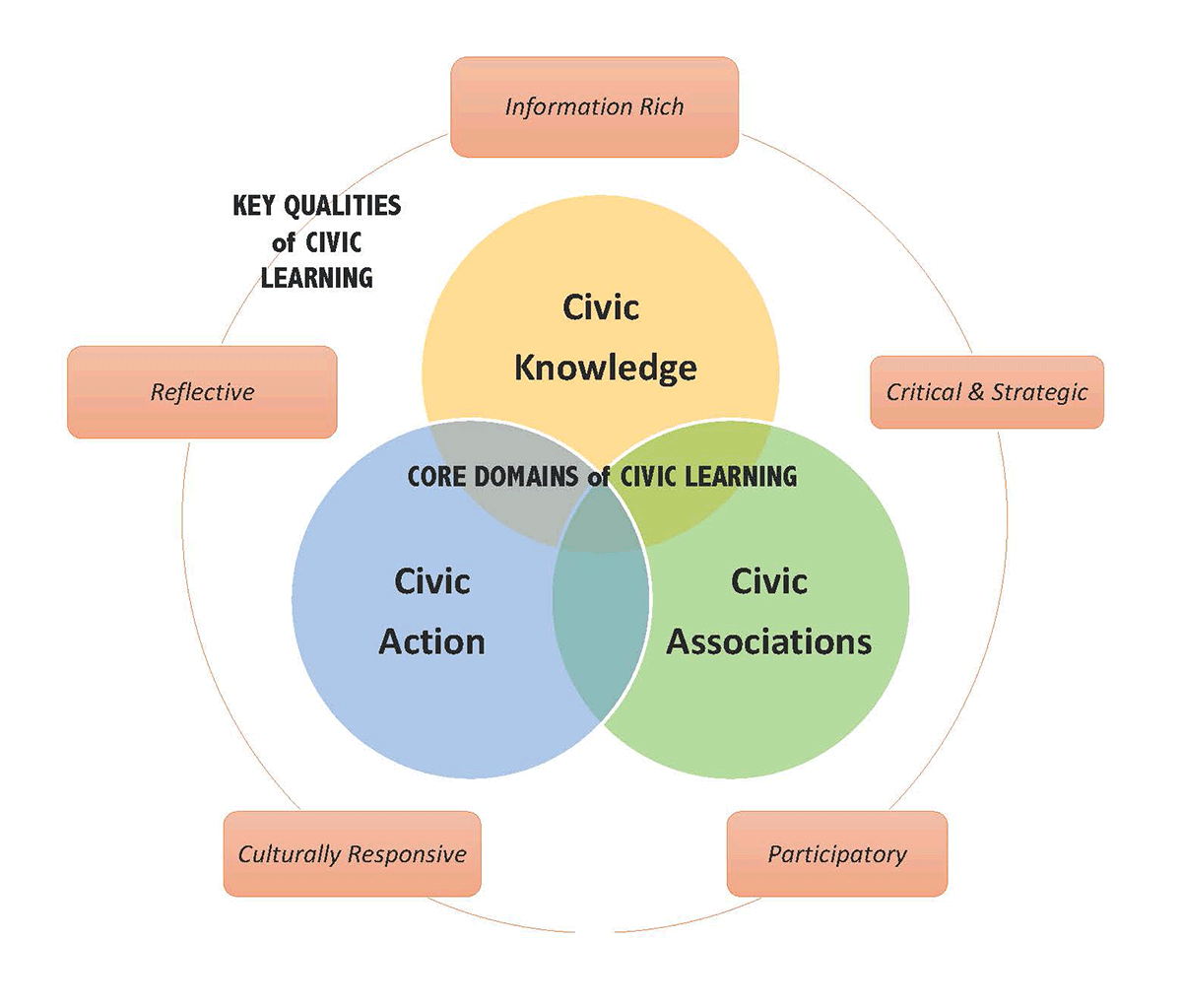
Drawing on these practices and research in the field, the LEADE framework of civic learning aims to promote civic knowledge, civic associations, and civic action. The LEADE framework also posits that high-quality civic learning is information rich, critical and strategic, participatory, culturally responsive, and reflective.
To read more about the LEADE framework and these features of high quality practice click here.